Differenze tra le versioni di "DChange Management"
(→Process) |
(→Process) (Etichetta: visualeditor) |
||
| Riga 181: | Riga 181: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | "Default" || A preliminary status which is displayed when a ''[[Glossary| | + | | "Default" || A preliminary status which is displayed when a ''[[Glossary|change]]'' is created. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | "Opened" || The ''[[Glossary| | + | | "Opened" || The ''[[Glossary|change]]'' has been recorded. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | "Requested" || The ''[[Glossary| | + | | "Requested" || The ''[[Glossary|change]]'' is confirmed and has been requested (it is a ''[[Glossary|request for change]]''). |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | "In Analysis" || The ''[[Glossary| | + | | "In Analysis" || The ''[[Glossary|change]]'' assessment and planning is ongoing. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | "Approval Requested" || The | + | | "Approval Requested" || The ''[[Glossary|change]]'' approval is submitted to the change authority. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | "Approved" || The | + | | "Approved" || The ''[[Glossary|change]]'' is approved for implementation. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | "Not Approved" || The | + | | "Not Approved" || The ''[[Glossary|change]]'' is not approved for implementation. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | "In Progress" || The | + | | "In Progress" || The ''[[Glossary|change]]'' implementation is ongoing. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | "Ready for Test" || The | + | | "Ready for Test" || The ''[[Glossary|change]]'' is ready for testing. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | "In Test" || The | + | | "In Test" || The ''[[Glossary|change]]'' testing is ongoing. |
|- | |- | ||
Versione delle 14:12, 22 mag 2015
Change Management process is supported by a SM workflow cartridge that enables the execution of the process according to the ITIL and ISO/IEC 20000 guidelines.
Of course the preconfigured process (the workflow cartridge) is just an accelerator and the tuning / completion of the initial configuration will still be required. To this aim, the Workflow Engine guide may be useful.
IMPORTANT NOTE: the configuration below is only one of the possible configuration to deal with the change management process. The need for a different behaviour of the process may be fulfilled by simple changes of the configuration.
Indice
- 1 Operational model
- 2 Roles
- 3 Process
- 4 Services
- 5 Management information
- 6 Views
- 7 Notifications
- 8 Reporting
- 9 Examples of use
- 9.1 Create and request a new problem as a technical team member
- 9.2 Assign a problem for resolution as a service manager
- 9.3 Monitor and control a problem as problem owner
- 9.4 Analyse and resolve a problem as a technical team member
- 9.5 Perform a major problem review as a service manager
- 9.6 Close a problem as a problem owner
Operational model
The preconfigured process has the objective to facilitate and support the effective and efficient execution of changes. At the core of the process configuration is the following operational model.
The requester, an authorized client, service manager, member of the service desk or technical team or n related process (such as Incident Management or Problem Management) requires to open a Request for Change (RfC). The service manager takes in charge it and assigns an owner who coordinates all the tasks needed to fulfil the change. The owner requests the change authorization to the change authority, if needed. As appropriate, technical team members may directly implement and deploy the change or make it through the Release Management process and later the Depolyment Change.
Roles
For this process, the following organizational roles are defined:
| Organizational role | Description | itmSUITE® role mapping | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Requester |
|
This role is mapped on: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change owner |
|
Role assigned by the service manager to himself/herself or to a technical team member. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical team member |
|
There are several technical teams predefined for different domains. The following table shows which users are members of each team.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical team manager |
|
There are several technical teams predefined for different domains. The following table shows which users are set as solution group manager for each domain.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service manager |
|
This role is mapped on a system resource with user of user type "Project/Service Manager". There are different service managers configured for specific services. See Services section in this page for further information. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change authority | This role is mapped based on the required authorization and change classification.
For change implementation authorization:
The CAB is mapped on a group: "CAB". For change deployment authorization:
|
Process
As for all workflows, new changes can be created by using the self service portal, accessible by means of Self Service menu.
The following requests which trigger a new instance of the change management process are configured and available to all organizational roles in the self service portal:
| Self service topic | Self service category | Self service request | Authorized roles |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Applications" | "itmCLOUD" | "Change" (open a change) | Requesters |
| "Personal Devices" | "Personal Computers" | "Change" (open a change) | Requesters |
| "Personal Devices" | "Peripherals" | "Change" (open a change) | Requesters |
| "Personal Devices" | "Telephony" | "Change" (open a change) | Requesters |
| "Network" | "Networking Management" | "Change" (open a change) | Requesters |
| "Technical Services" | "Server Management" | "Change" (open a change) | Requesters |
A change may also be automatically opened during the execution of other processes by the resources dealing with them.
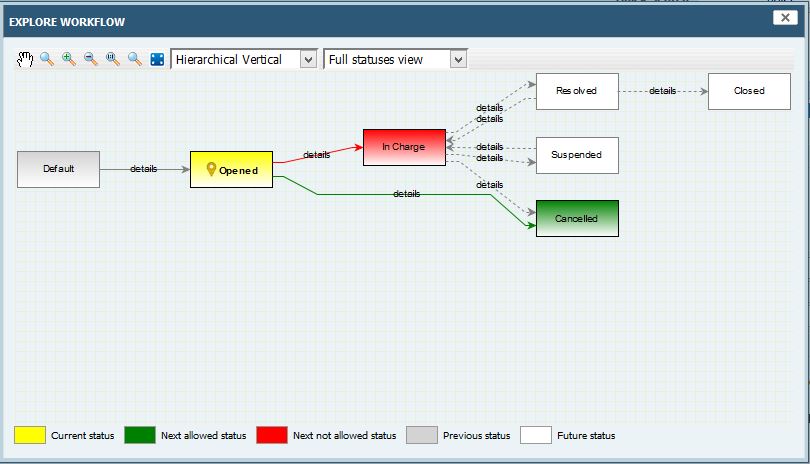
A workflow is configured to support the change management process. The workflow is characterized by workflow statuses and workflow transitions. The figure below illustrates the process.
The table below explains the meaning of each workflow status.
| Workflow status | Description |
|---|---|
| "Default" | A preliminary status which is displayed when a change is created. |
| "Opened" | The change has been recorded. |
| "Requested" | The change is confirmed and has been requested (it is a request for change). |
| "In Analysis" | The change assessment and planning is ongoing. |
| "Approval Requested" | The change approval is submitted to the change authority. |
| "Approved" | The change is approved for implementation. |
| "Not Approved" | The change is not approved for implementation. |
| "In Progress" | The change implementation is ongoing. |
| "Ready for Test" | The change is ready for testing. |
| "In Test" | The change testing is ongoing. |
| "Ready for Deployment" | The plan to implement the problem resolution is executed. A change may be opened at this stage. |
| "Deployed" | The plan to implement the problem resolution is executed. A change may be opened at this stage. |
| "In Review" | The plan to implement the problem resolution is executed. A change may be opened at this stage. |
| "Cancelled" | The problem is not confirmed and, therefore, cancelled. |
| "Suspended" | The problem execution is temporarily suspended. In this status service levels calculation are suspended too. |
| "Aborted" | The plan to implement the problem resolution is executed. A change may be opened at this stage. |
| "Closed" | The problem closure has been confirmed. No other changes are possible. |
And finally the table below explains the roles authorized to execute the workflow transitions.
| Source status | Destination status | Authorized executors | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Default" | "Opened" | Requesters, technical team members, service managers. | See the self service portal configuration previously described. |
| "Opened" | "Requested" | Requester, service manager. |
|
| "Opened" | "Cancelled" | Requester, service manager. | |
| "Requested" | "Opened" | Requester, service manager.. | |
| "Requested" | "Cancelled" | Requester, service manager. | |
| "Requested" | "Suspended" | Service manager. | |
| "Suspended" | "Requested" | Service manager. | |
| "Problem Assigned" | "Problem in Analysis" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Problem Assigned" | "Suspended" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Suspended" | "Problem Assigned" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Problem Assigned" | "Cancelled" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Problem in Analysis" | "Suspended" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Suspended" | "Problem in Analysis" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Problem in Analysis" | "Problem in Resolution" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Problem in Resolution" | "Problem in Analysis" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Problem in Analysis" | "Cancelled" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Problem in Resolution" | "Cancelled" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Problem in Resolution" | "Resolved" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Problem in Resolution" | "Suspended" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Resolved" | "Major Problem Review" | Automatic | The workflow transition is automatically performed when the field Major Problem is set to "Yes". |
| "Requested" | "Problem Assigned" | Service manager. | |
| "Major Problem Review" | "Closed" | Problem owner, service manager. | Any related incident is set to closed (workflow status "Resolved" in incident management) and any related known error is unpublished (workflow status "Known Error Unpublished" in known error management). |
| "Suspended" | "Problem in Resolution" | Problem owner, service manager. | |
| "Resolved" | "Closed" | Requester, problem owner, service manager. | Any related incident is set to closed (workflow status "Resolved" in incident management) and any related known error is unpublished (workflow status"Known Error Unpublished" in known error management). |
Related processes
Several other IT Service Management processes are related to the problem management one. Some basic interfaces are provided. The tab Related Items of the problem and, in particular, the sub tab Tickets of it allows to view all the existing between the problem and other processes (managed through tickets).
Incident management
It is possible to create a problem from the incident management process or to relate an existing problem to an incident and vice versa.
Change management
It is possible to create a new change, managed via the change management process. The GENERATE CHANGE command allows to instantiate a new change by copying some problem information and by creating a relationship between the problem and the generated change.
Asset management and configuration management
It is possible to relate configuration items to a problem by using the tab Related Items and, in particular, the sub tab Configuration Items. The ASM and/or CMS modules features are made available here (e.g. view of configuration item details, configuration exploration or impact analysis).
Known error management
It is possible to create a new known error, managed via the known error management process. The GENERATE KE command allows to instantiate a new known error by copying some problem information and by creating a relationship between the problem and the generated knonw error.
Release and deployment management
A release may include the solution of one or more problems even if this may happen rarely (more frequently a release includes changes generated to resolve problems and related to them, The relationship between a release and and problems is more frequently created working from the release. In any case, this can be done from the tickets tab Related Items and, in particular, the sub tab Configuration Items by using the ADD EXISTING or SELF SERVICE commands.
Services
Different services are configured for different problem domain areas as illustrated in the following table.
| Incidents domain areas | Service | Service manager |
|---|---|---|
| Application management | Only one application, and the related service ("itmCLOUD") is configured. | The user "servicemanager" is configured as service manager. |
| Personal devices management | "Personal Device Management". | The user "personalmanager" is configured as service manager. |
| Network management | "Network Management" | The user "netmanager" is configured as service manager. |
| Server management | "Server Management" | The user "servermanager" is configured as service manager. |
Management information
Many management information are available as fields in the problem management configured form. The following table illustrates the intended use of key information and its behaviour. NOTE: information are available (visible) and can be modified according to a specific configuration which is meant to be suitable for the organizational roles involved in the process.
| Information group or tab | Field | Purpose | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Information | Ticket Op Status | To show the operational status of the problem, see workflow statuses in Process section of this page. | Status changes are performed by means of the Save&Next command. |
| General Information | Request Name | To show the SRCS request invoked | |
| General Information | Short Description | To provide a short description of the problem. | Always visible. |
| General Information | Requester | To identify the name of the requester (who has requested the problem). | A list is presented, influenced by.... TBC |
| General Information | Creation Date | To show the date and time the problem was created. | This information is automatically recorded and cannot be manually changed. See History tab for more detailed tracking information. |
| General Information | Edit Date | To show the date and time the problem was last updated. | This information is automatically recorded and cannot be manually changed. See History tab for more detailed tracking information. |
| General Information | Creation User | To show the user who created the problem. | This information is automatically recorded and cannot be manually changed. See History tab for more detailed tracking information. |
| General Information | Edit User | To show the user who updated the problem last. | This information is automatically recorded and cannot be manually changed. See History tab for more detailed tracking information. |
| Ticket Classification | Project/Service | To show the service (or project) to which the problem is related. | This is automatically set at open time and can't be modified. |
| Ticket Classification | Ticket Type | To show the type of workflow executed. | This is automatically set at open time and can't be modified. |
| Ticket Classification | Problem type | To enter the information whether the problem is reactive (opened as a consequence of one or more incidents) or proactive (opened to avoid potential incidents). | |
| Ticket Classification | Problem Classification | To set the problem classification information (domain).This is used for statistic reasons. | The classification information initially provided can be changed. |
| Ticket Classification | Major Problem | To show if the problem has to be considered major or not. | This impacts the need of a final review (if major) or not. |
| Prioritisation & Planning | Required Solution Date | To provide the date of solution requested by the Requester. | This is normally set for reactive problems, according to the related incidents priorities and status. |
| Prioritisation & Planning | User Priority | To provide the priority given to the problem by the Requester. | A four level scale is set but it can be changed. |
| Prioritisation & Planning | Ticket Urgency | To define the urgency for the resolution. | A three level scale is set but it can be changed. |
| Prioritisation & Planning | Ticket Impact | To define the impact on the business of the problem. | A four level scale is set but it can be changed. |
| Prioritisation & Planning | Ticket Priority | To view the calculated priority of the problem. | The priority is automatically set based on Ticket Urgency and Ticket Impact. The driving matrix can be configured. |
| Prioritisation & Planning | Forecast Solution Date | To set the forecasted resolution date and time for the problem. | |
| Ownership and Groups | Master SG | To define the supervising team. | This is set by the service manager and mandatory from the Ticket Op Status "Problem Assigned".
The team may change during the problem life cycle. |
| Ownership and Groups | Solution Group | To define the team to which the problem is assigned for analysis and/or resolution. | This is set by the service manager and mandatory from the Ticket Op Status "Problem Assigned".
The team may change during the problem life cycle. |
| Ownership and Groups | Owner | To define who is the problem owner who should monitor the lifecycle of the problem. | This is set by the service manager and mandatory from the Ticket Op Status "Problem Assigned". He/she can be changed by the service manager and the Owner him/herseilf. |
| Ownership and Groups | Ticket Worker | To set the resource who shall work in order to analyse and/or resolve the problem. | If the analysis is performed by the problem owner, the Ticket Worker is normally not set. He/she is a member of the team defined in the Solution Group field.However setting him/her is not mandatory. Alternatively, it is possible to assign specific tasks to resources by using the Ticket Activities tab. |
| Ticket Details | Description | To provide a more detailed description of the problem. | An auto tracking field is used enabling to view the user who has updated. |
| Ticket Details | Analysis | To provide the analysis of the cause(s) of the problem. | This field is only visible to service desk and technical team members.
An auto tracking field is used enabling to view the user who has updated. |
| Ticket Details | Solution | To describe the solution applicable to the problem. | This field is only visible to service desk and technical team members.
An auto tracking field is used enabling to view the user who has updated. |
| Ticket Details | Comments | To provide comments helpful for the analysis and/or resolution of the problem or for future memory (e.g. continual improvement).. | This field is only visible to service desk and technical team members.
An auto tracking field is used enabling to view the user who has updated. |
| Ticket Details | Comments for Requester | To provide comments to the requester of the problem. | An auto tracking field is used enabling to view the user who has updated.
This field is not the only way to interact with the requester. To this aim messages, manage via the Messages tab, can be very useful |
Fields can be mandatory to save the incident in some workflow statuses. These fields are highlighted with a red asterisk.
Views
The following views are made available in the Tickets area of the home page:
| View | Content | Requester | Problem owner | Technical team | Service manager |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Problems resolved | Problems in statuses "Resolved", "Major Problem Review". | X | |||
| Problems requested | Problems in status "Requested". | X | |||
| Problems owned | Problems in status "Problem Assigned", "Problem in Analysis", "Problem in Resolution", "Resolved" and "Major Problem Review" where Owner is the logged resource. | X | |||
| Problems routed to my team | Problems in status "Problem Assigned", "Problem in Analysis", "Problem in Resolution" where Solution Group is the solution group to which the logged resource belongs to. | X | |||
| Problems assigned to me | Problems in status "Problem Assigned", "Problem in Analysis", "Problem in Resolution" where the Ticket Worker is the logged resource. | X | |||
| Problems suspended | Problems in status "Suspended". | X | X | ||
| Major problems to review | Problems in status "Major Problem Review". | X | X |
Additionally, the following views are made available in the Problem menu for all the organizational roles:
| View | Content |
|---|---|
| Problems active | Problems in status "Requested", "Problem Assigned", "Problem in Analysis", "Problem in Resolution", "Resolved" and "Major Problem Review". |
| Problems suspended | Problems in status "Suspended |
| Problems closed | Problems in status "Closed" |
| Problems cancelled | Problems in status "Cancelled" |
Notifications
The following notifications are configured:
| Trigger | Recipients | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| A problem is requested | Service manager | Alert that there is an problem to assign for resolution. |
| A problem is assigned a owner | Problem owner | Alert that the problem was assigned to him/her. |
| A solution group is assigned or changed for the problem | Solution group manager | Alert that there are resource(s) to allocate to manage the problem. |
| A problem review shall be executed (the problem is in workflow status "Resolved" and the Major Problem field is set to "Yes") | Problem owner, service manager | Alert that a problem review is to be done. |
| An problem is resolved | The problem creator, the requester | Alert that the problem is resolved. |
| A ticket worker is assigned | The assigned ticket worker | Alert that there is work to be done. |
| A problem is suspended | The problem creator, the requester, the service manager, the problem owner | Alert that the problem is suspended. |
| An problem is closed | The problemc reator, the requester, the service manager, the problem owner | Alert that the problem has been closed. |
| An incident is cancelled | The problem creator, the requester, the service manager, the problem owner | Alert that the problem has been cancelled. |
Reporting
A set of standard reports are made available for the problem management process. It is not required to have the REP module to use them, however the module is required if new or changed reports are needed. The available reports are placed under Problem/Reporting menu.
The following table lists the reports available by default and their visibility:
| Report name | Content | Access |
|---|---|---|
| Problem per priority - trend | An histogram showing the problem volumes per priority monthly trend. | Service managers and technical team members. |
| Problem per priority - volume | A pie containing the split of problems per priority. | Service managers and technical team members. |
| Problem per service - trend | An histogram showing the problem volumes per service monthly trend. | Service managers and technical team members. |
| Problem per service - volume | A pie containing the split of problems per service. | Service managers and technical team members. |
| Problem per service/priority - volume | An histogram showing the incidents volume per service and priority. | Service managers and technical team members. |
| Problem - assign time | A pie showing the percentage of problems respecting the target defined for the take "assign time"* objective (the time elapsed from the "Requested" to the "Problem Assigned" workflow status. | Service managers and technical team members. |
| Problem per priority - resolution time | An histogram showing, per priority, the percentage of problems respecting the target defined for the "Resolution time"* objective (the time elapsed from the "Problem Assigned" to the "Resolved" workflow status. | Service managers and technical team members. |
* "Assign time" and "Resolution time" objectives are defined within the OCE module.
A basic form of reporting is also provided by views. Views basically allow to list problems and their attributes but may also be configured to calculates sums, averages on some of them. The available views are illustrated in the dedicated section of this page.
Examples of use
In this section some examples of use of the configured problem management process are given.
If you get lost, any time use the EXPLORE WORKFLOW command of the problem management form. This enables to view the status of the workflow as shown in the figure below. By clicking on a relationship between workflow statuses, roles and users enabled to perform it are presented.
NOTE: the EXPLORE WORKFLOW command is available only if the ticket is first saved.
For more information on how to use any workflows, including incident management, please refer to the workflow execution guide.
Create and request a new problem as a technical team member
- Login as "appspecialist" user
- Activate the Self Service menu
- Choose a self service topic, self service category and finally "Problem" as self service request (this determines the creation of a new problem)
- Fill the problem form, at least with mandatory form and save with the SAVE command
You have now saved the problem, take note of the ticket number for further reference or use.
Assign a problem for resolution as a service manager
- Login as "servicemanager"
- Open the the desired problem; you can do it quickly either by
- Access the "Problems Requested" view in the Tickets area of the home page and pick a problem
- Access the Problem/Problems active menu and pick a problem in workflow status "Requested" among those listed
- Insert the reference number of a problem in workflow status "Requested" in Quick Search, after selecting the search context "Ticket"
- Assign the key roles
- Fill the problem form with Owner, Solution Group and, may be, Master Solution Group, Ticket Worker,
- Pressing the SAVE & NEXT command, choose the "1. Assign ticket" workflow transition
The problem is now in workflow status "Problem Assigned".
Monitor and control a problem as problem owner
- Login as a user owning a problem (see assign a problem for resolution as a service manager described previously)
- Open the desired problem; you can do it quickly either by
- Access the views in the Tickets area of the home page and pick a problem among those listed in workflow status "Problem Assigned", "Problem in Analysis", "Problem in Resolution" where the user is owner
- Access the Problem/Problems active menu and pick a problem among those listed in workflow status "Problem Assigned", "Problem in Analysis", "Problem in Resolution" where the user is owner
- Insert the reference number of a problem in workflow status "Problem Assigned", "Problem in Analysis", "Problem in Resolution" where the user is owner in Quick Search, after selecting the search context" Ticket"
- Update some fields (e.g. Analysis or Solution)
- Pressing the SAVE & NEXT command, choose a transition to update the workflow status
Analyse and resolve a problem as a technical team member
- Login as a technical team member working on the problem (see assign a problem for resolution described previously)
- Open a problem in status "Problem in Analysis"; you can do it quickly either by
- Access the views in the Tickets window of the home page and pick a problem among those listed in workflow status "Problem in Analysis"
- Access the Problem/Problems active menu and pick a problem in workflow status "Problem in Analysis"
- Insert the reference number of a problem in workflow status "Problem in Analysis"
- Optionally update problem information (for example Analysis and Solution fields)
- Save the problem by pressing SAVE command
- Send a message to the problem owner to notice the progress you made (use the tab Messages of the ticket).
Perform a major problem review as a service manager
- Login as "servicemanager"
- Open the the desired problem; you can do it quickly either by
- Access the view "Major Problem to Review"in the Tickets window of the home page and pick a problem
- Access the Problem/Problems active menu and pick a Problem among those listed in workflow status "Major Problem Review"
- Insert the reference number of a problem in workflow status "Major Problem Review" in Quick Search, after selecting the search context "Ticket"
- Update some fields (e.g. Comments, or add a review report as attachment)
- Pressing the SAVE & NEXT command, choose the "1. Close" workflow transition
The problem is now in workflow status "Closed".
Close a problem as a problem owner
- Login as a user owning a problem (see assign a problem for resolution as a service manager described previously) which is not major
- Open the the desired problem (one which is not major); you can do it quickly either by
- Access the "Problems resolved" view in the Tickets area of the home page and pick a problem among those listed where the user is owner
- Insert the reference number of an problem in workflow status "Resolved" where the user is owner in Quick Search, after selecting the search context "Ticket"
- Close the problem by
- Pressing the SAVE & NEXT command
- Choosing the "1. Close" workflow transition
The problem is now in workflow status "Closed".